CEPHEIDS, NEBULAE AND PULSARS
October 17, 2023 2023-10-18 14:44CEPHEIDS, NEBULAE AND PULSARS
In this material, important terms for UPSC Prelims examination like Neutron star, Cepheids, Nebulae and Pulsars are given. Happy Preparation!
NEUTRON STARS
- Neutron stars are formed when a massive star runs out of fuel and collapses. The very central region of the star – the core – collapses, crushing together every proton and electron into a neutron.
- If the core of the collapsing star is between about 1 and 3 solar masses, these newly-created neutrons can stop the collapse, leaving behind a Neutron Star. (Stars with higher masses will continue to collapse into stellar-mass black holes.)
- Most Neutron Stars are found spinning wildly with extreme magnetic fields as pulsars or magnetars.
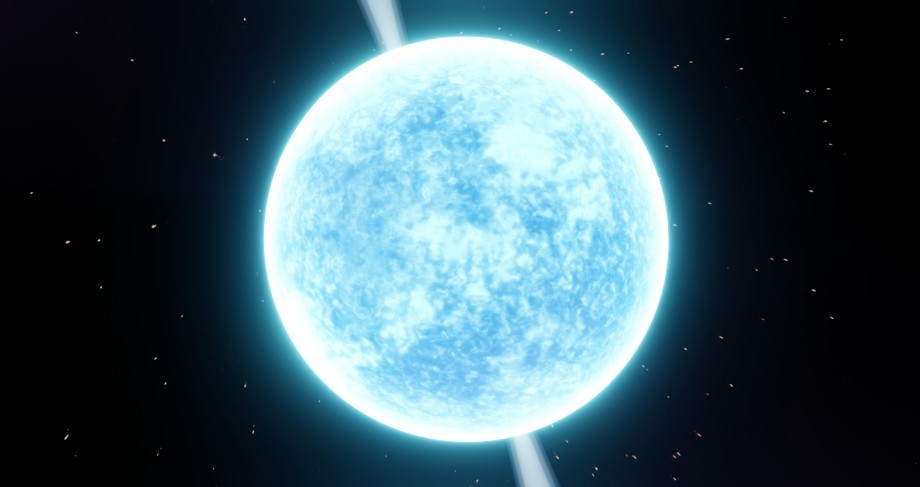

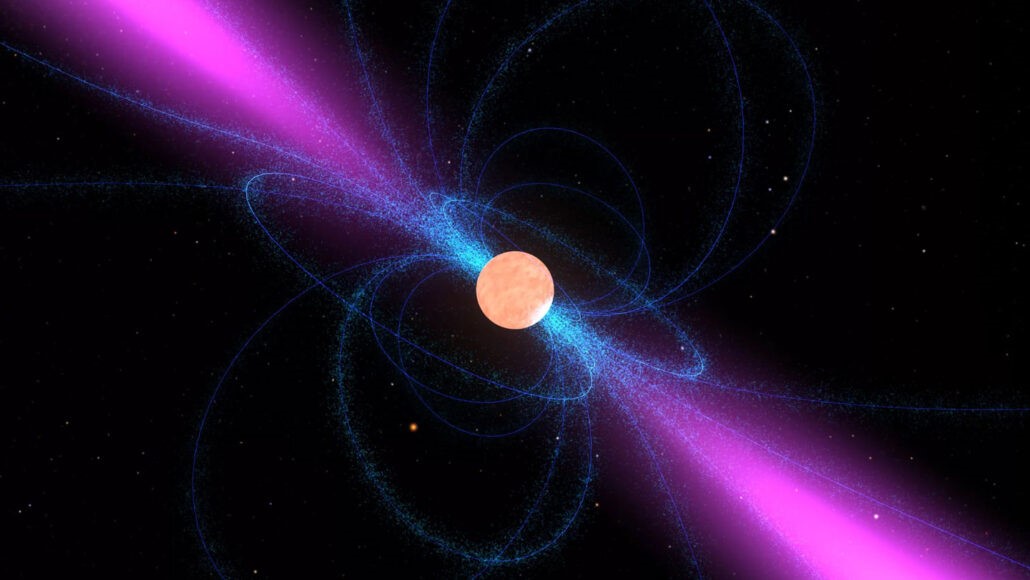
PULSARS
- Pulsars are rapidly rotating neutron stars that blast out pulses of radiation at regular intervals ranging from seconds to milliseconds.
- Packing a mass that could be more than that of our sun in the space of about a large city, pulsars are spherical and compact.
- Pulsars have very strong magnetic fields which funnel jets of particles out along the two magnetic poles. These accelerated particles produce very powerful beams of light.
- Often, the magnetic field is not aligned with the spin axis, so those beams of particles and light are swept around as the star rotates. When the beam crosses our line-of-sight, we see a pulse, in other words, we see pulsars turn on and off as the beam sweeps over Earth.
- Thus, in effect, pulsars can be thought of as ‘cosmic lighthouses’.
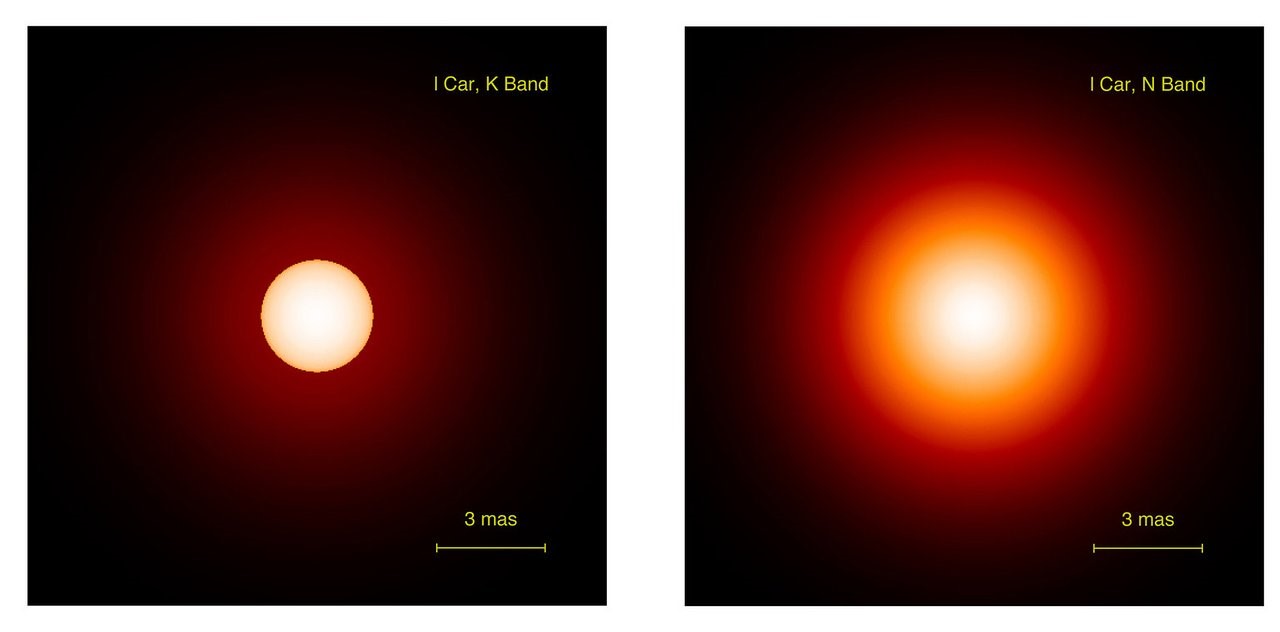
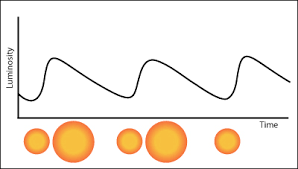
CEPHEIDS
- Any star whose observed light varies (luminosity) notably in intensity is Variable Star. The changes in brightness may be periodic, semiregular, or completely irregular.
- Cepheids, also called Cepheid Variables, are stars which brighten and dim periodically.
- They are very luminous stars, 500 to 300,000 times greater than the sun, with short periods of change that range from 1 to 100 days.
- Their periods of variation (i.e., the time for one cycle) are closely related to their luminosity.
- In fact, Cepheids are very special variable stars because their period is
- regular (that is, does not change with time), and a uniform function of their brightness.
- Therefore, they’re useful in measuring interstellar and intergalactic distances reliably.
- Astronomers can identify them not only in our Galaxy, but in other nearby galaxies as well. If one requires the distance to a given galaxy one first locates the Cepheid variables in this galaxy. From these observations one determines the period of each of these stars.

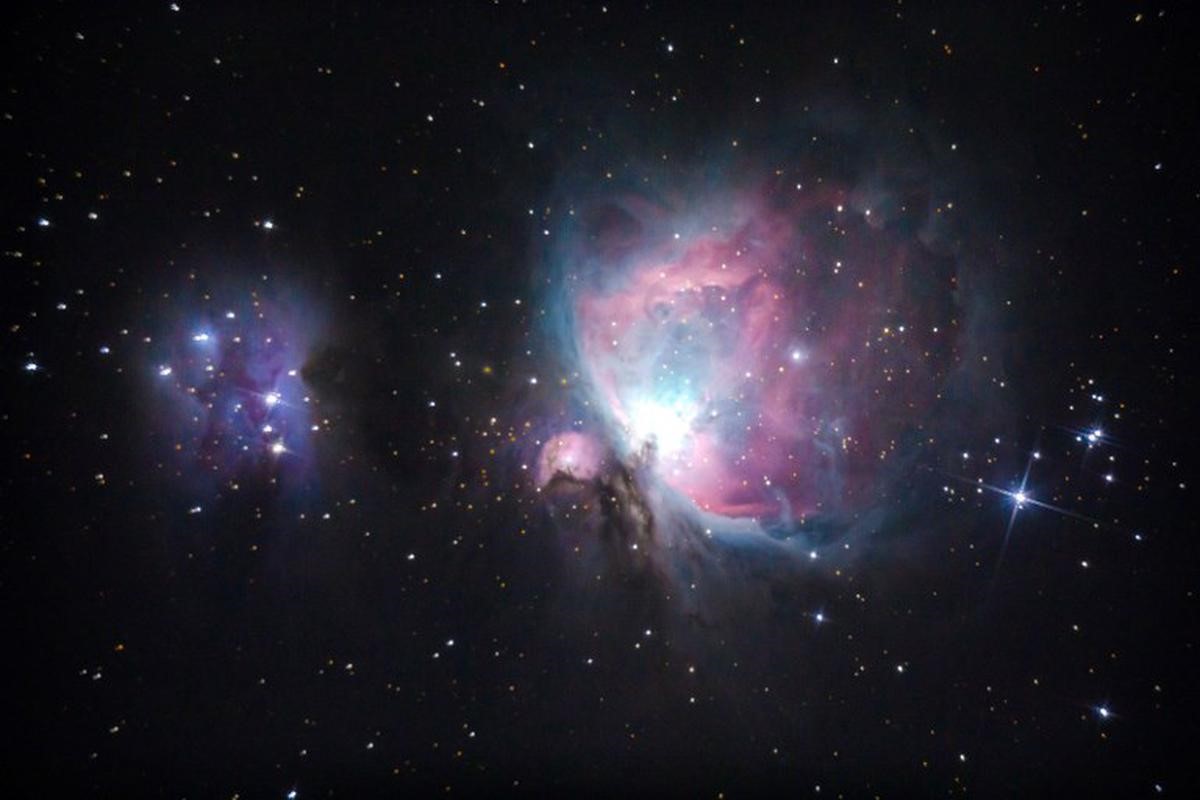
NEBULAE
- Nebulae are interstellar clouds of gas and dust, mostly hydrogen and helium.
- Some nebulae (more than one nebula) come from the gas and dust thrown out by the explosion of a dying star, such as a supernova.
- Other nebulae are regions where new stars are beginning to form. For this reason, some nebulae are called “star nurseries.”
- The dust and gases in a nebula are very spread out, but gravity can slowly begin to pull together clumps of dust and gas. As these clumps get bigger and bigger, their gravity gets stronger and stronger. This process can later lead to star formation and planet formation.


Watch the video explanation of the topic ‘Cepheids, Pulsars, Nebulae and Neutron star’.
To UPSC-standard MCQs, join our Telegram Channel.
To get years of subjectwise-segregated newspaper articles, join our subjectwise Telegram Channels.
Join our 140k+ YouTube community to watch free classes on various UPSC related topics.
Follow us on Instagram for UPSC updates.
Click here to read more UPSC Current Affairs.
Ekam IAS is the oldest online IAS institute in Kerala. We’ve years of experience in mentoring and teaching students all over the nation, helping them achieve their UPSC-dream through the right guidance, strategy, and precise content. Join Ekam IAS and turn your UPSC-dream into reality.
To learn customizable preparation strategies, book an appointment with our UPSC-expert. Book Now.