KAVERI RIVER
October 8, 2023 2023-10-08 20:14KAVERI RIVER
- Kaveri River, also spelled as Cauvery, is a sacred river of South India.
- It is sometimes called as Dakshin Ganga (Ganga of the South).
- The Cauvery River is one of the major rivers of the peninsula. It is the third largest river in South India after Godavari and Krishna.
- The Cauvery basin extends over states of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala and Union Territory of Puducherr
- Physiographically, the basin can be divided into three parts – the Western Ghats, the Plateau of Mysore, and the Delta.
- Red soils occupy large areas in the basin. Alluvial soils are found in the delta areas.
- It carries water throughout the year with comparatively less fluctuation than the other Peninsular rivers. This is because the upper catchment area receives rainfall during the southwest monsoon season (summer) and the lower part during the northeast monsoon season (winter).
- Its uppermost course is tortuous, with a rocky bed and high banks under luxuriant vegetation.
ORIGIN
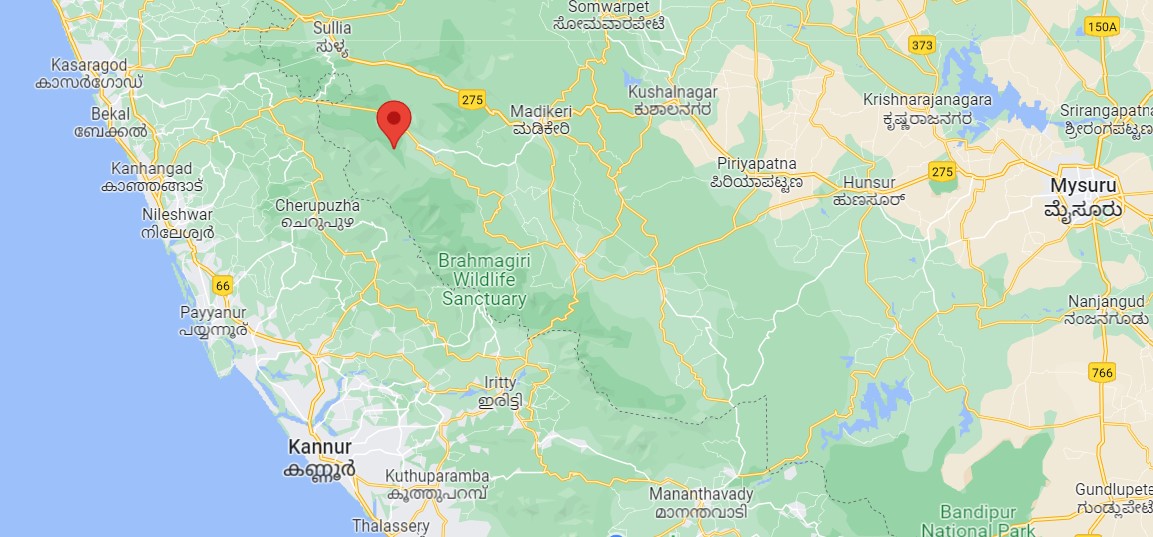
The Kaveri rises in Brahmagiri hills (1,341m) of Kogadu district in Karnataka. Its length is 800 km and it drains an area of 81,155 sq. km.
Talakaveri or Talacauvery is the place that is generally considered to be the source of the river Kaveri and a holy place for many Hindus. It is located on Brahmagiri hills near Bhagamandala in Kodagu district. It is located close to the border with Kasaragod district (Kerala).
The temple here, built in Kerala style, is dedicated to Goddess Kaveriamma. A tank (kundike) seen on the hillside, which is said to be the origin. The river originates underground to emerge as the Kaveri river some distance away.
THE FLOW OF RIVER KAVERI
The River Cauvery originates at Talakaveri in Coorg District of Karnataka in Brahmagiri Range of hills in the Western ghats at an elevation of 1341 m.
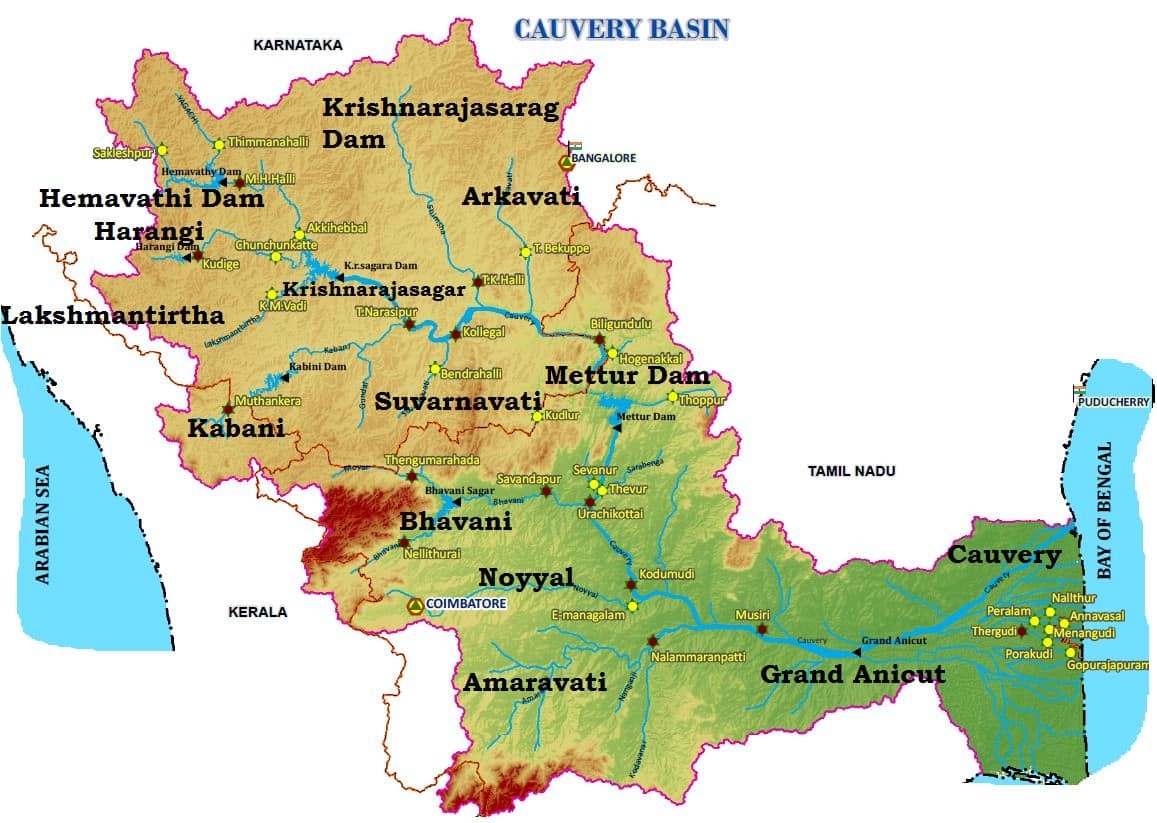
At the Krishnaraja Sagara, the Kaveri is joined by two tributaries, the Hemavati and Lakshmantirtha, and dammed for irrigation.
In Karnataka the river bifurcates twice, forming the sacred islands of Srirangapatnam (last Anglo-Mysore war was fought here) and Sivasamudram, 50 miles (80 km) apart.
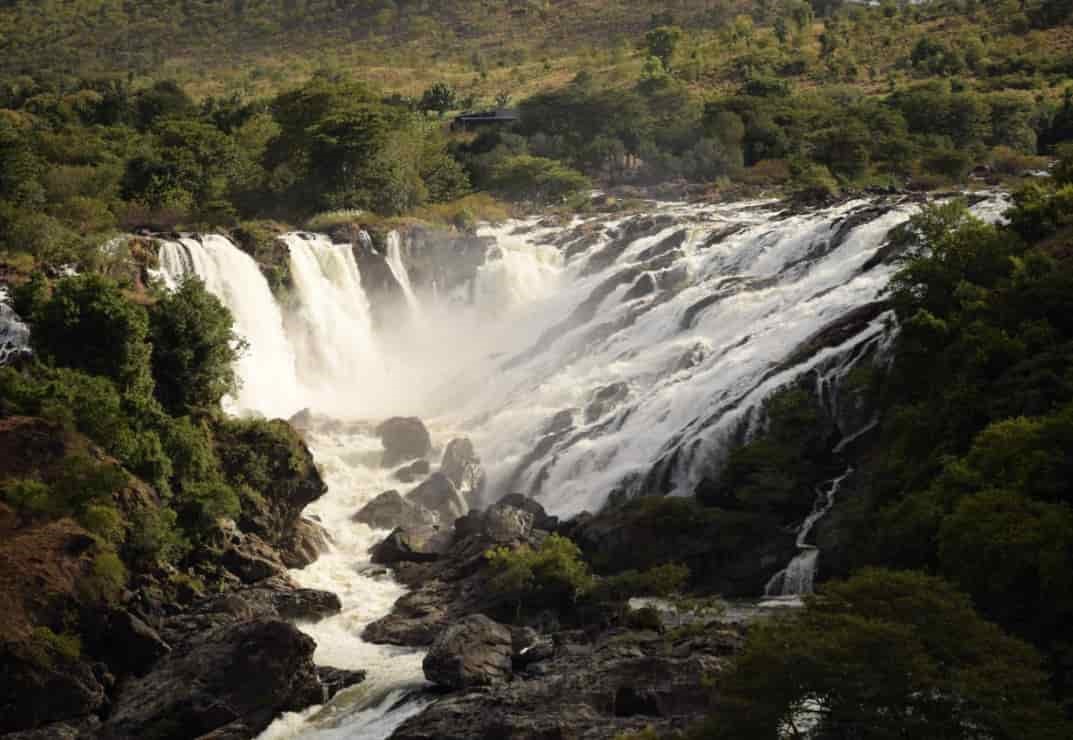
Around Sivasamudram are the scenic Sivasamudram Falls, comprising two series of rapids, Bhar Chukki and Gagana Chukki, plunging a total of 320 feet (100 metres) and reaching a width of 1,000 feet (300 metres) in the rainy season.
After branching in Shivanasamudram, the two branches of the river join after the fall and flow through a wide gorge which is known as “Mekedatu”(Goats leap) and continues its journey to form the boundary between Karnataka and Tamil Nadu States for a distance of 64 Kms.The falls supply hydroelectric power to Mysuru (Mysore), Bengaluru (Bangalore), and the Kolar Gold Fields, more than 100 miles (160 km) away.
At Hogennekkal Falls, it takes Southernly direction and enters the Mettur Reservoir which was constructed in 1934. A tributary called Bhavani joins Cauvery on the Right bank about 45 Kms below Mettur Reservoir. Thereafter it takes Easterly course to enter the plains of Tamil Nadu.
Near Erode, the river Kaveri is joined by Bhavani, Noyil and Amaravati.
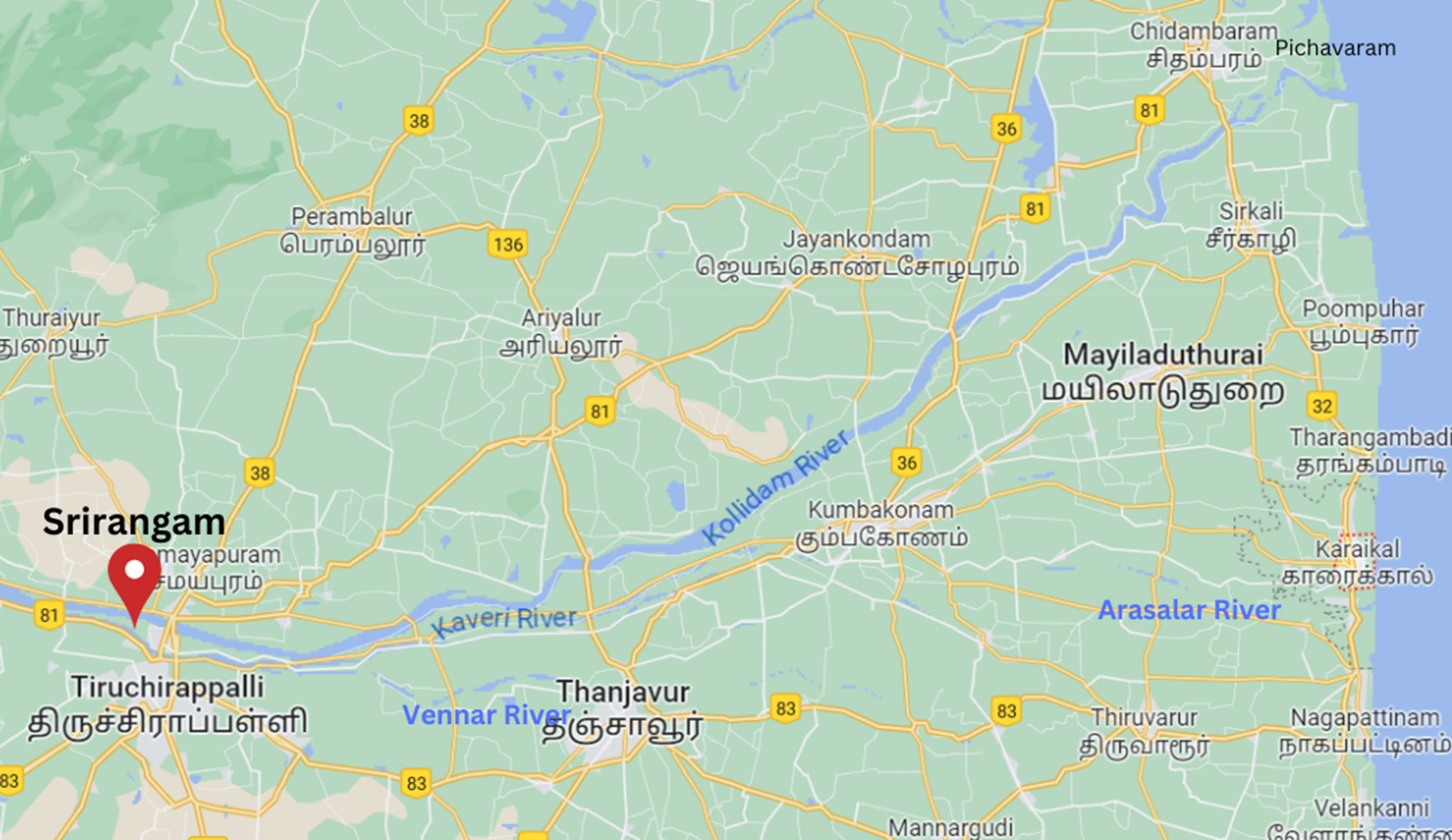
Immediately after crossing Tiruchirapalli district, the river divides into two parts, the Northern branch being called “The Coleron” and Southern branch remains as Cauvery and from here the Cauvery Delta begins.
After flowing for about 16 Kms, the two branches join again to form “Srirangam Island”.
On the Cauvery branch lies the “Grand Anicut” said to have been constructed by a Chola King in 1st Century A.D.
Below the Grand Anicut, the Cauvery branch splits into two, Cauvery and Vennar. These branches divide and sub-divide into small branches and form a network all over the delta.
Before emptying into the Bay of Bengal south of Cuddalore, Tamil Nadu, the river breaks into a large number of distributaries forming a wide delta called the “garden of southern India.”
The river Kaveri falls into Bay Bengal near Poompuhar.
BOUNDARY
It is bounded on the west by the Western Ghats, on the east and south by the eastern Ghats and on the north by the ridges separating it from the Tungabhadra and Pennar basins.
TRIBUTARIES
- Major left bank tributaries are Harangi, the Hemavati, the Shimsha and the Arkavati
- Major right bank tributaries are Lakshmantirtha, the Kabbani, the Suvarnavati, the Bhavani, the Noyil and the Amaravati.
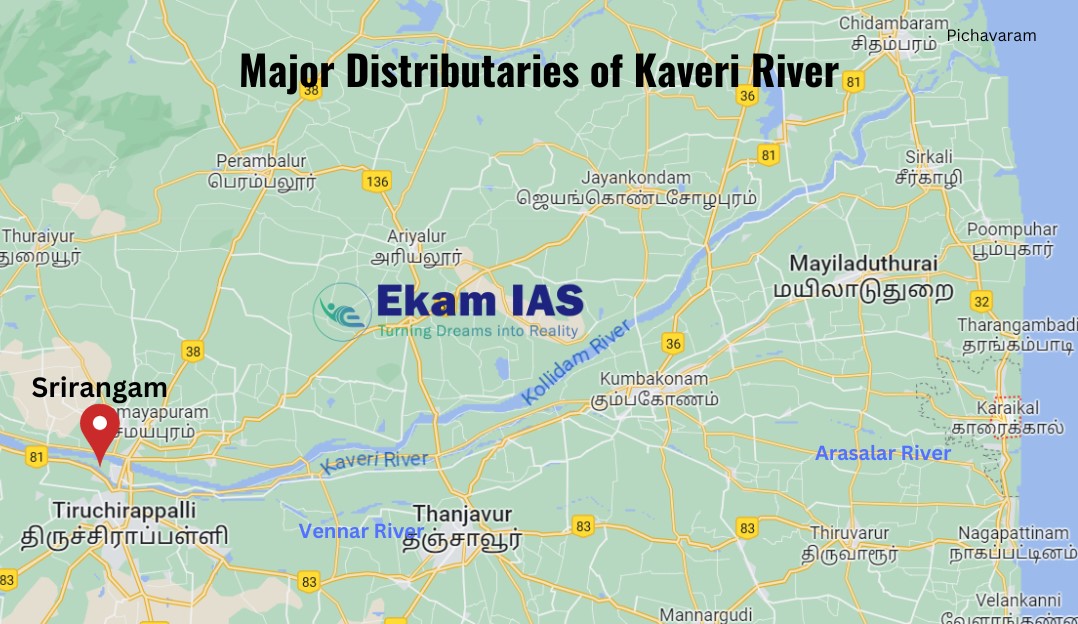
DISTRIBUTARIES
Major distributaries are Kollidam River (Coleroon R), Vennar River and Arasalar River.
MAJOR DAMS IN KAVERI
- Krishnaraja Sagara Dam
- Mettur Dam
- Kallanai Dam (Grand Anicut)
ISLAND FORMED AS RIVER BIFURCATES:
Srirangapatnam (Karnataka), Sivasamudram (Karnataka) and Srinagam (Tamil Nadu).
MAJOR PLACES
Some of the major places through which Kaveri river passes are Mysore, Erode, Salem, Tiruchirappali, Thanjavur and Mayiladuthurai
WATERFALLS
Major waterfalls located on Kaveri river are Sivasamudram falls and Hoggenekkal falls.

PROTECTED AREAS IN KAVERI BASIN
- Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve: Part of Wayanad, Nagarhole, Bandipur and Madumalai, Nilambur, Silent Valley and Siruvani hills in Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka.
- Protected Areas in Karnataka
- Bandipur National Park: Kabini,
- Nagarhole National Park: Kabini
- Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary
- Bheemeshwari Wildlife Sanctuary
- Biligiri Rangaswamy Temple Tiger Reserve: Bhargavi River that flows here is a tributary of Cauvery.
- Protected Areas in Tamil Nadu
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Cauvery North Wildlife Sanctuary
- Cauvery South Wildlife Sanctuary (Declared in 2022)
- Hogenakkal Wildlife Sanctuary
- Protected Areas in Kerala
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
- Silent Valley National Park
URBAN CENTRES AND INDUSTRIES
The city of Bangalore is situated just outside this basin. Important industries in the basin include cotton textile industry in Coimbatore and Mysore, cement factories in Coimbatore and Tiruchirappali and industries based on mineral and metals. The Salem steel plant and many engineering industries in Coimbatore and Tiruchirappali are also situated in this basin.
Download the PDF Now
Watch the video explanation of the topic ‘Kaveri River’.
To UPSC-standard MCQs, join our Telegram Channel.
To get years of subjectwise-segregated newspaper articles, join our subjectwise Telegram Channels.
Join our 140k+ YouTube community to watch free classes on various UPSC related topics.
Follow us on Instagram for UPSC updates.
Click here to read more UPSC Current Affairs.
Ekam IAS is the oldest online IAS institute in Kerala. We’ve years of experience in mentoring and teaching students all over the nation, helping them achieve their UPSC-dream through the right guidance, strategy, and precise content. Join Ekam IAS and turn your UPSC-dream into reality.
To learn customizable preparation strategies, book an appointment with our UPSC-expert. Book Now.